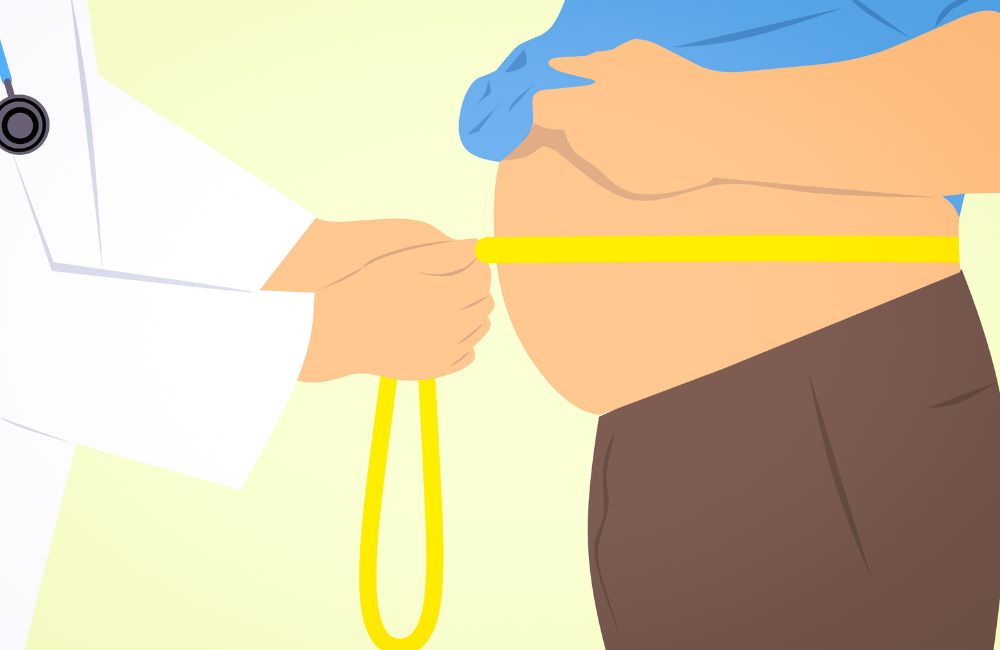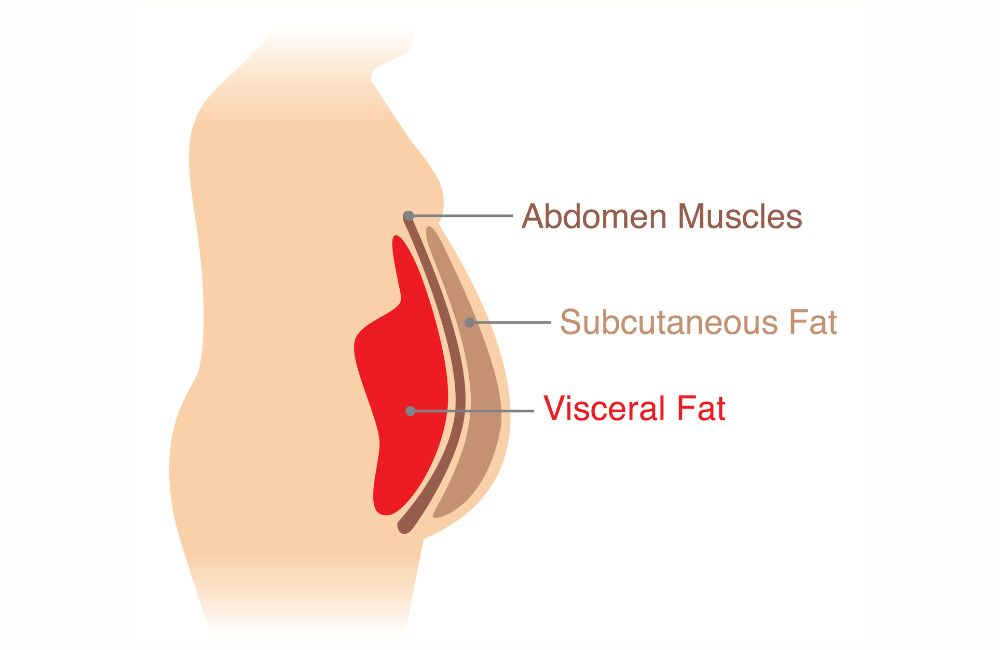
Visceral fat, stored within your abdominal cavity and arteries, poses risks to health including diabetes and heart disease.
While some body fat is normal, not all fat is the same.
Located near vital organs like the liver, stomach, and intestines, visceral fat is often termed “active fat” due to its role in health issues.
Not all belly fat is visceral; subcutaneous fat found just beneath the skin, is also common in areas like the arms and legs.
Unlike subcutaneous fat, visceral fat resides within the abdominal cavity, making it less visible but more impactful on health.
You may also like:
- How To Lose 50 Pounds as Quickly as Possible: 5 Simple Steps, Backed by Science
- 7 Best Exercises to Lose Belly Fat After 50, Trainer Says
The Importance of Fat

Firstly, it’s crucial to acknowledge that fat is an essential component of our bodies, necessary for our survival. Without any fat, our bodies cannot function properly and may even face life-threatening consequences.
Nevertheless, excessive fat can lead to various health issues, including cardiovascular, neurological, and orthopedic complications. Fat serves multiple purposes, including energy storage, insulation for warmth, and protection for our internal organs.
Visceral Fat: A Hazard to Health
While fat is indispensable for our well-being, excess fat, particularly visceral fat, poses significant health risks. Visceral fat surrounds our organs and has been linked to elevated risks of diabetes and certain cancers. Therefore, reducing visceral fat is crucial for improving overall health.
Effective Fat Loss Strategies
In general, creating a caloric deficit—consuming fewer calories than you expend through physical activity—is the most effective method for losing fat. However, achieving this deficit can be challenging due to factors like food cravings and limited knowledge about exercise techniques.
Nevertheless, by implementing some of the straightforward tips provided in this section, you can gradually and steadily lose weight, improving your overall health in the process.
1. Perform High-Intensity Workouts

The more intense your workout is, the more calories you’ll burn. That being said, higher-intensity workouts can also put you at greater risk for injury. For this reason, it’s important that you don’t try to do too much, or too fast.
When it comes to the type of exercise, research points to the benefit of engaging in cardiovascular workouts as opposed to resistance training. This seems to burn more calories, leading to greater weight loss.
2. Eat a Clean Diet

On the other end of the spectrum, diet is incredibly important for fat loss. By following a clean, strict diet, you can shed pounds one day at a time.
Unfortunately, there is much disagreement about which type of diet is best. Some people advocate for a vegan diet. Others point to a carnivore diet. Still, others will swear by a ketogenic diet or something else entirely.
Whatever diet you follow for weight loss, you need to keep a few things in mind.
- You should monitor your calorie intake closely.
- Working with a dietitian or nutritionist can help you stay on track.
- Avoiding “empty” calories (such as those found in alcohol or pure sugar) is always a good idea.
Other than that, many people find success with many different types of diets.
3. Prioritize Protein Intake

Of the three macronutrients (carbs, proteins, and fats), protein is the most satiating. This means that protein leaves us feeling more full than fats and carbs do.
Therefore, ensuring adequate protein intake goes a long way toward weight loss.
Protein can be found in high amounts in animal products such as chicken and beef. However, there is at least a small amount of protein in almost every food on earth.
For minimal health, it’s recommended that individuals eat 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. However, athletes and those looking to lose weight may want to increase this level slightly.
Conclusion
Losing weight is hard no matter who you are. But by following the advice listed above, you’ll put yourself in a great position for healthy, sustainable weight loss. If you are ready to commit to a plan to lose your visceral fat and improve your health, try these tips out today!
Works Cited
- Elffers, T. W., de Mutsert, R., Lamb, H. J., de Roos, A., Willems van Dijk, K., Rosendaal, F. R., Jukema, J. W., & Trompet, S. (2017). Body fat distribution, in particular visceral fat, is associated with cardiometabolic risk factors in obese women. PloS one, 12(9), e0185403. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185403
- Chait, A., & den Hartigh, L. J. (2020). Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine, 7, 22. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2020.00022
- Crudele, L., Piccinin, E., & Moschetta, A. (2021). Visceral Adiposity and Cancer: Role in Pathogenesis and Prognosis. Nutrients, 13(6), 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13062101
- Willis, L. H., Slentz, C. A., Bateman, L. A., Shields, A. T., Piner, L. W., Bales, C. W., Houmard, J. A., & Kraus, W. E. (2012). Effects of aerobic and/or resistance training on body mass and fat mass in overweight or obese adults. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 113(12), 1831–1837. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01370.2011


