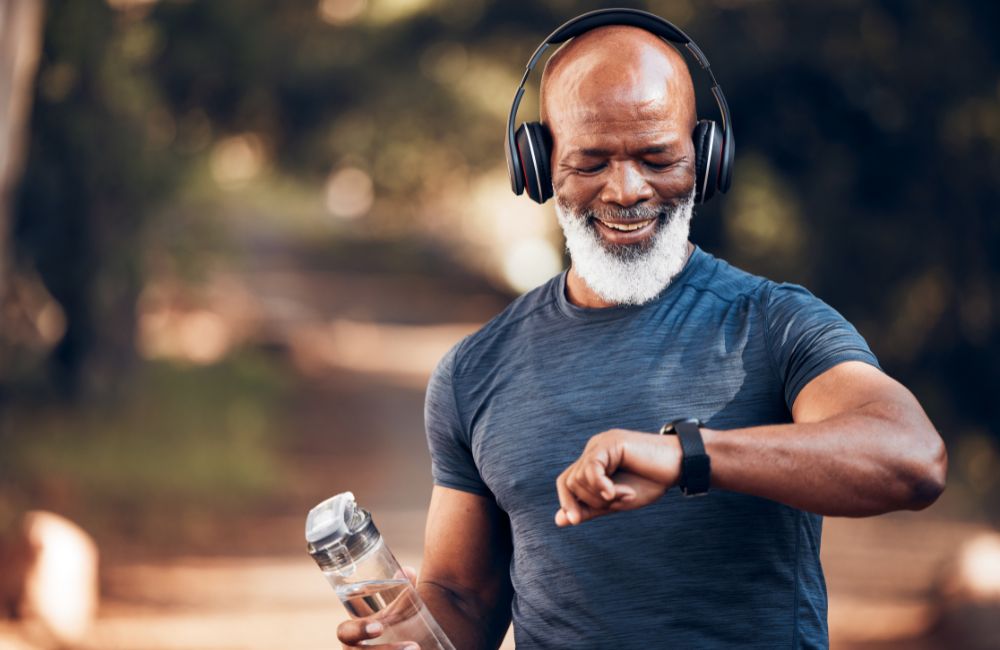
As we age, maintaining a regular exercise routine becomes increasingly crucial for overall health and longevity. Cardiovascular exercise, in particular, plays a vital role in promoting heart health, maintaining weight, and enhancing overall well-being.
However, determining the appropriate amount of cardio for seniors aged 60 and above requires consideration of various factors.
In this article, we will explore the science-backed guidelines on how much cardio seniors should do after 60 and delve into the numerous benefits of incorporating cardiovascular exercise into their daily lives.
Scientific Studies on Cardio for Seniors:
Several scientific studies have shed light on the positive impact of cardio exercises on seniors. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) indicated that regular moderate-intensity aerobic exercise significantly reduced the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes in older adults.
Additionally, a meta-analysis published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that consistent cardio workouts improved cognitive function and reduced the risk of cognitive decline in older individuals.
Determining the Right Amount of Cardio
The American Heart Association recommends that seniors aged 60 and above engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
This can be achieved through various activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing. It’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of workouts, considering individual fitness levels and any pre-existing health conditions.
Benefits of Cardio after 60:
- Heart Health: Regular cardiovascular exercise strengthens the heart, improves blood circulation, and lowers the risk of heart disease and related conditions.
- Weight Management: Cardio workouts help burn calories, maintain a healthy weight, and prevent age-related weight gain.
- Cognitive Function: Studies suggest that cardio exercises enhance brain health, memory, and cognitive abilities, reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
- Mood and Mental Well-being: Cardio releases endorphins, boosting mood, reducing stress, and alleviating symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Bone Health: Weight-bearing cardio activities help maintain bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis in seniors.
Conclusion
Engaging in regular cardio exercises after 60 offers numerous health benefits, from improving heart health and cognitive function to enhancing mood and overall well-being. Based on scientific research, seniors should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise each week.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, and remember to listen to your body, adjusting workouts as needed. Embrace the joy of staying active and reap the rewards of a healthy and fulfilling life through regular cardiovascular exercise.